A Bar Code is a system for storing and displaying integrated data such as price, model, and manufacturer in a format composed of bars and spaces of varying widths. Bar codes are often seen in retail environments. The bar code can also be found on industrial products, or on delivery request forms for home and office deliveries – their uses are wide-ranging.
In order to read the bar code, there is a wide variety of scanners available, each designed for a specific purpose. Let’s take a look at a bar code in more detail:
Bar Code Structure
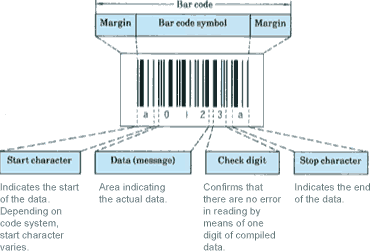
Margin:
Spaces, normally white, where nothing printed are required at each end of the code and they should be 10 times that of a narrow bar.
Bar code symbol:
The area composed of bars and spaces is known as the “bar code symbol”.
Bar code:
The symbol together with the left and right margins make up what is called bar code.
The Kind of Bar Code
There are multiple kinds of barcodes and utilized in a variety of applications.
- UPC=Universal Product Code (Standardized in the USA)
- EAN=European Article Number (Standardized in Europe based on UPC)
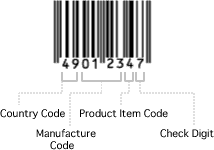
In Japan, JAN (Japanese Article Number) is used as one of EAN and regulated as JIS-X-0501 (in 1987) EAN (JAN) is composed of 13 digits (standard) or 8 digits. On the other hand, UPC is composed of 12 digits or 7 digits (including a check digit) In Japan, it is labeled on grocery and other stuff and mainly utilized in POS (Point Of Sales) field.
Country Code is assigned to each country as Composition of POS codes are universal. For instance, 49 and 45 are assigned to Japan.
Manufacturer Code is registered by Manufactures* applying to chamber of commerce in each government.
Product Item Code is put and determined by each manufacturer.
Check Digit is a value calculated from country, manufacturer, and product item codes and gives higher credibility of data.

CODABAR(NW-7)
NW-7 has easy to print module composition and used for tugs of courier service and envelopes of photo development.Processable data is numbers (0~9), symbols (-,$,:,/,+,.), start and stop characters (a~d).
ITF(Interleaved 2 of 5)
ITF is suitable for high density printing and used for logistics (packaging boxes) and miniature labels on small stuff such as jewelry. It is standardized as logistics code in 1987 (JIS-X-0502).

CODE39
CODE39 is printable in Alphabets and employed by US Ministry of Defense in MIL standard. It is also used worldwide in FA field such as AIAG tugs, ODETTE tugs, and EIAJ tugs. Processable data are numbers (0~9), symbols (-,space,$,/,+,%,.),alphabets (A~Z) and start and stop character (*).

CODE128
CODE128 enables to output data in ASCI code (128 kinds) and used in FA and OA fields. Processable data are full ASCII (128 characters), start characters (3 kinds), stop character, non-data function characters (4 kinds), and code setting and selecting characters (4 kinds).

